LDPE (Low Density Polyethylene) masterbatch is a granular product made by adding various functional additives or pigments to LDPE as a carrier, widely used in the plastic processing industry.
Types of LDPE masterbatch
LDPE (low-density polyethylene) masterbatch can be divided into the following common types based on their functions and uses:
Ordinary filling masterbatch
Introduction: This is the most common type of LDPE masterbatch, mainly composed of LDPE resin, fillers such as calcium carbonate, and a small amount of additives.
Features: By adding fillers, the cost of plastic products can be reduced while maintaining the original properties of LDPE, such as flexibility and water resistance.
Usage: Widely used in fields such as film, pipe, injection molded products, etc., it effectively reduces production costs without affecting the basic performance of the product. For example, in agricultural films, adding an appropriate amount of ordinary filling masterbatch can reduce raw material costs while ensuring the film’s insulation, transparency, and other properties.
Functional masterbatch
Anti-aging masterbatch
Introduction: Adding functional additives such as UV absorbers and antioxidants to LDPE resin can improve the aging resistance of plastic products.
Features: Effectively absorbs ultraviolet rays, inhibits oxidation reactions, delays the aging and brittleness of plastic products during long-term use, and extends their service life.
Usage: Commonly used plastic products for outdoor use, such as agricultural film, sunshade nets, wire and cable sheaths, etc. Taking agricultural film as an example, after adding anti-aging masterbatch, the agricultural film can be used in outdoor environment for a long time without cracking and fading, ensuring the stable growth environment of crops.
Smooth masterbatch
Introduction: It generally contains lubricants such as oleic acid amide and erucic acid amide, which can reduce the friction coefficient on the surface of plastic products.
Features: Make plastic products have good smoothness, improve their processing performance and usability. During the processing, it can reduce the adhesion between films and improve production efficiency; Easy to open and use the product during use.
Usage: Mainly used in the fields of film, pipe, etc. For example, adding smooth masterbatch to packaging film can make the film easier to transport and process on the packaging production line, and also make it convenient for consumers to open the packaging when using it.
Opening masterbatch
Introduction: It is usually made by mixing inorganic fillers (such as diatomaceous earth, talcum powder, etc.) and LDPE resin to improve the opening performance of films.
Characteristics: In the film production process, it can effectively prevent film adhesion, make the film have good openness, and facilitate subsequent processing and use.
Usage: Widely used in the production of various plastic films, such as food packaging films, agricultural films, etc. Taking food packaging film as an example, adding open masterbatch can prevent the film from sticking together during the packaging process, ensuring smooth packaging.

Coloring masterbatch
Introduction: Made by mixing high concentration pigments or dyes with LDPE resin carrier, used to add color to plastic products.
Characteristics: It has good dispersibility, heat resistance, and migration resistance, which can make plastic products obtain uniform and bright colors, and the color is not easy to fade or migrate during processing and use.
Usage: Suitable for various LDPE plastic products that require coloring, such as toys, stationery, packaging containers, etc. For example, in toy manufacturing, using colored masterbatch can give toys a rich and diverse range of colors, attract children’s attention, and ensure the safety and stability of colors.
Formula ratio
The ratio of LDPE masterbatch may vary depending on the type of masterbatch, specific application requirements, and manufacturer. The following are examples of common proportioning ranges for different types of LDPE masterbatch:
Ordinary filling masterbatch
LDPE resin: usually accounts for 30% -70%. Generally, LDPE resin with high melt index and good flowability is selected to better encapsulate fillers and have good formability during processing.
Fillers: mainly calcium carbonate, accounting for 30% -70%. The particle size and surface treatment method of calcium carbonate can affect the performance of the masterbatch. Fine grained calcium carbonate can improve the mechanical properties and appearance quality of the product. Surface treated calcium carbonate has better compatibility with LDPE resin.
Additives: The content of dispersants, coupling agents and other additives is usually around 0.5% -5%. Dispersants help to evenly disperse fillers in resins, while coupling agents can enhance the bonding force between fillers and resins, improving the overall performance of masterbatch.
Functional masterbatch
Anti-aging masterbatch
LDPE resin: accounting for about 70% -90%.
UV absorbers: generally 1% -5%. It can effectively absorb ultraviolet rays, protect LDPE products from UV damage, and delay the aging process.
Antioxidants: Content is around 0.5% -3%. Cooperating with UV absorbers, it prevents resin oxidation reactions during processing and use, further improving the aging resistance of the product.
Other additives, such as dispersants, lubricants, etc., account for about 0.5% -2% and are used to improve the processing performance and stability of masterbatch.
Smooth masterbatch
LDPE resin: usually accounts for 60% -80%.
Slippery agents: mainly oleic acid amide, erucic acid amide, etc., with a content of 10% -30%. The amount of lubricant added directly affects the smoothness performance of plastic products. An appropriate amount of lubricant can significantly reduce the friction coefficient of the product surface and improve its processing and usage performance.
Other additives: including antioxidants, dispersants, etc., accounting for about 1% -5%, to prevent the lubricant from oxidizing during processing and ensure uniform dispersion of the lubricant in the resin.
Opening masterbatch
LDPE resin: accounting for 50% -70%.
Inorganic fillers: such as diatomaceous earth, talc powder, etc., accounting for 30% -50%. These inorganic fillers can form tiny protrusions on the surface of the film, preventing film adhesion and improving opening performance.
Additives: including dispersants, anti-static agents, etc., with a content of 1% -5%, help to disperse inorganic fillers and further improve the surface properties of the film.
Coloring masterbatch
Pigments or dyes: Depending on the depth and concentration of the desired color, they generally account for 1% -20%. High concentration pigments can be used to produce masterbatch with bright and dark colors, while low concentration pigments are suitable for products with light colors or low color requirements.
LDPE carrier resin: accounting for 70% -95%. The performance of carrier resin has a significant impact on the dispersion of pigments and the processing performance of masterbatch. LDPE resin with good compatibility and flowability with the product resin is usually selected.
Dispersant: Content is around 1% -10%. Dispersants can reduce the surface tension between pigment particles, evenly disperse them in the carrier resin, and improve the coloring effect and appearance quality of the product.
Other additives, such as lubricants, antioxidants, etc., account for about 0.5% -5% and are used to improve the processing performance and storage stability of masterbatch.
The above ratios are for reference only. In actual production, adjustments and optimizations need to be made based on specific product requirements, raw material characteristics, and production processes to achieve the best product performance and economic benefits.
Production process of different types of LDPE masterbatch
The production process of different types of LDPE masterbatch has similarities in the basic process, but there may be differences in specific formulas, additives, and processing parameters. The following are the general production processes for ordinary filling masterbatch, functional masterbatch, and coloring masterbatch:
Ordinary filling masterbatch
1. Raw material preparation: The main raw materials are LDPE resin, calcium carbonate and other fillers, as well as a small amount of additives (such as dispersants, coupling agents, etc.). LDPE resin should be selected according to product performance requirements, and calcium carbonate needs to be pre treated to improve its compatibility and dispersibility with the resin.
2. Mixing and stirring: Add LDPE resin, calcium carbonate, and additives in a certain proportion to a high-speed mixer for thorough mixing. By stirring, the fillers and additives are evenly distributed on the surface of the resin particles, preparing for subsequent processing.
3. Melt extrusion: The mixed material enters the twin-screw extruder and undergoes melt extrusion at a certain temperature and screw speed. The temperature setting of the extruder is usually determined based on the melting point and flowability of LDPE resin, typically between 150-200 ℃. During the extrusion process, the rotation of the screw causes the material to undergo shear and compression, further mixing evenly and expelling air.
4. Cooling granulation: The extruded material is formed into strips or filaments through the die head, and then enters the cooling water tank for cooling and shaping. The cooled material is then cut into particles of a certain size by a granulator to obtain ordinary filling masterbatch.
Functional masterbatch
1. Raw material selection and formula design: according to different functional requirements, select corresponding functional additives (such as ultraviolet absorber and antioxidant in anti-aging masterbatch, oleamide and erucic amide in smooth masterbatch, etc.), and make reasonable formula design with LDPE resin. The amount of functional additives added needs to be determined based on the specific performance requirements and usage environment of the product.
2. Mixing and dispersion: LDPE resin is mixed with functional additives in a high-speed mixer or internal mixer. In order to evenly disperse the additives in the resin, it may be necessary to add some dispersants or use special mixing processes. For some difficult to disperse additives, pre-treatment methods can also be used, such as making the additives into mother liquor or performing surface treatment.
3. Melt blending and extrusion: Similar to ordinary filling masterbatch, the mixed material is sent into a twin-screw extruder for melt blending and extrusion. During the extrusion process, it is necessary to strictly control parameters such as temperature, screw speed, and residence time to ensure that functional additives are thoroughly mixed with LDPE resin and form a stable structure. For example, in the production of anti-aging masterbatch, too high temperature may lead to the decomposition of UV absorbers and other additives, affecting the performance of masterbatch.
4. Cooling and granulation: The extruded material is cooled and shaped in a cooling water tank, and then cut into granules by a granulator. For some functional masterbatch with special requirements for particle shape and size, special granulation equipment and processes may be required, such as underwater granulation or air-cooled granulation.
Coloring masterbatch
1. Pigment selection and pretreatment: Choose the appropriate pigment or dye based on the desired color and the requirements for the use of plastic products. Pigments need to have good properties such as heat resistance, light resistance, dispersibility, and migration resistance. In order to improve the dispersibility of pigments in resins, it is usually necessary to pre treat the pigments, such as grinding, surface treatment, etc., to achieve a certain particle size requirement.
2. Selection of carrier resin: Choose a resin with good compatibility and moderate flowability with LDPE as the carrier. Generally, LDPE resin with a higher melt index is selected to better encapsulate and disperse pigments during processing.
3. Ingredients and Mixing: Add pigments, carrier resins, and appropriate additives (such as dispersants, lubricants, etc.) in a certain proportion to a high-speed mixer for thorough mixing. During the mixing process, it is necessary to ensure that the pigment is evenly distributed in the carrier resin to avoid pigment aggregation or uneven dispersion.
4. Melt extrusion and granulation: The mixed material enters the twin-screw extruder for melt extrusion. During the extrusion process, the pigment is further refined and uniformly dispersed in the carrier resin through the shearing and squeezing action of the screw. The temperature and screw speed parameters of the extruder should be adjusted according to the characteristics of the pigment and resin to ensure the smooth progress of the extrusion process and product quality. The extruded material is processed through cooling, granulation, and other processes to produce colored masterbatch.
In actual production, different manufacturers may adjust and optimize their production processes based on their own equipment conditions, product quality requirements, and production experience to produce LDPE masterbatch products with stable performance and reliable quality.
Production equipment
The equipment for producing LDPE masterbatch mainly includes raw material processing equipment, mixing equipment, extrusion equipment, cooling equipment, granulation equipment, etc. The following is a specific introduction:
1. Raw material processing equipment
Drying machine: used for drying LDPE resin and other raw materials to remove moisture and volatile substances. Because the moisture in the raw materials can affect the quality of the masterbatch, resulting in problems such as bubbles and surface defects in the product. Common drying machines include hot air circulation drying machines, dehumidification drying machines, etc.
Screening equipment: such as vibrating screens, rotary vibrating screens, etc., used to screen solid raw materials such as fillers and pigments, remove impurities and large particles, ensure the uniformity of raw material particle size, and prevent the performance and processing stability of masterbatch from being affected by uneven raw material particle size.
2. Hybrid equipment
High speed mixer: It is a device that preliminarily mixes LDPE resin, fillers, additives and other raw materials. It achieves uniform mixing of materials in a short period of time through high-speed rotating stirring blades, and can also raise the temperature appropriately during the stirring process to better bond the additives with the resin surface and improve the mixing effect.
Internal mixer: For some formulas that require more thorough mixing and dispersion, especially for the production of functional masterbatch containing difficult to disperse additives or requiring higher mixing uniformity, internal mixer is a commonly used equipment. It uses two relatively rotating rotors to strongly shear, squeeze, and knead materials in a sealed chamber, achieving a highly uniform mixing state.
3. Extrusion equipment
Twin screw extruder: It is one of the core equipment for LDPE masterbatch production. It has good mixing, plasticizing, and extrusion capabilities, which can fully melt and mix materials uniformly under high temperature, high pressure, and high shear force, and extrude them into the desired shape. Its screw structure is complex and can be designed and combined according to different process requirements to meet the needs of various masterbatch production.
Single screw extruder: In some situations where production efficiency is not high or the masterbatch formula is relatively simple, single screw extruders are also used. It has a simple structure and easy operation, but its mixing and plasticizing ability is relatively weak, making it suitable for ordinary filling masterbatch or coloring masterbatch with lower production requirements.
4. Cooling equipment
Cooling water tank: used for cooling and shaping extruded strip-shaped or filamentous materials. Usually, circulating water cooling is used, and the water temperature is generally controlled between 15-30 ℃ to ensure that the material can cool quickly and prevent problems such as deformation and adhesion.
Air cooling device: For some special requirements of masterbatch, such as functional masterbatch that should not come into contact with water during the cooling process, an air cooling device can be used. By using forced air cooling to cool the material, the air cooling speed is relatively slow, but it can avoid the influence of moisture on the performance of the masterbatch.
5. Granulation equipment
Granulator: Cut the cooled material into granules of a certain size. There are two common types of pelletizers: hot pelletizers and cold pelletizers. Hot cutting machine is used to cut materials in a thermoplastic state, suitable for high viscosity and difficult to cool materials; Cold granulator is a widely used cutting method that cuts materials after they have completely cooled, resulting in regular particle shapes and better quality.
6. Auxiliary equipment
Measuring equipment: including electronic scales, measuring pumps, etc., used to accurately measure the amount of various raw materials added, ensuring the accuracy and stability of the masterbatch formula.
Conveyor equipment: such as screw conveyors, belt conveyors, etc., used to transport raw materials from storage areas to production equipment, as well as to transport finished masterbatch to packaging areas, achieving automated production processes.
Packaging equipment: There are automatic packaging machines, sealing machines, etc. used to package the produced LDPE masterbatch for storage and transportation. Packaging equipment can be selected according to packaging specifications and requirements, such as particle packaging machines for small packaging and ton bag packaging machines for large packaging.
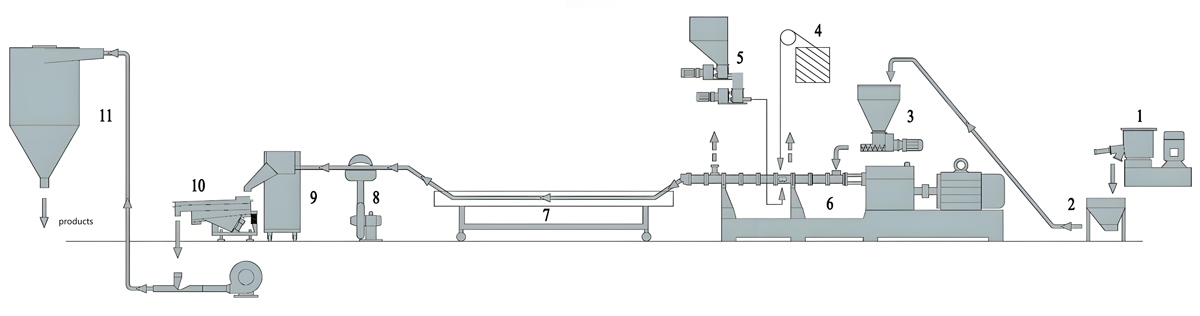
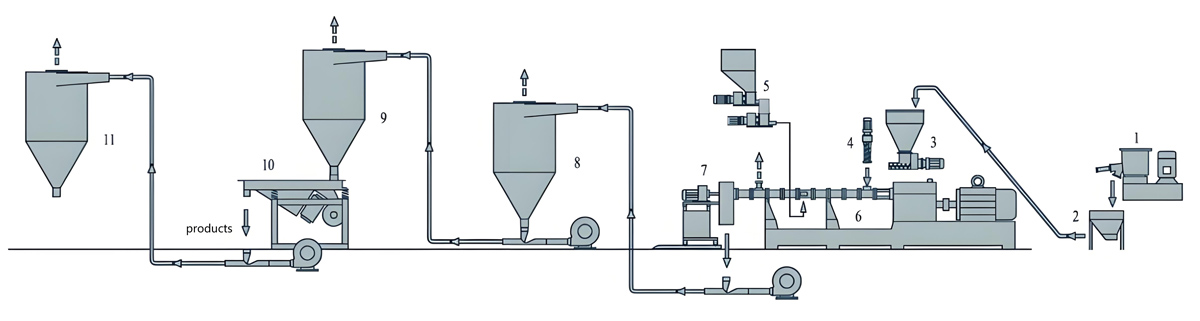
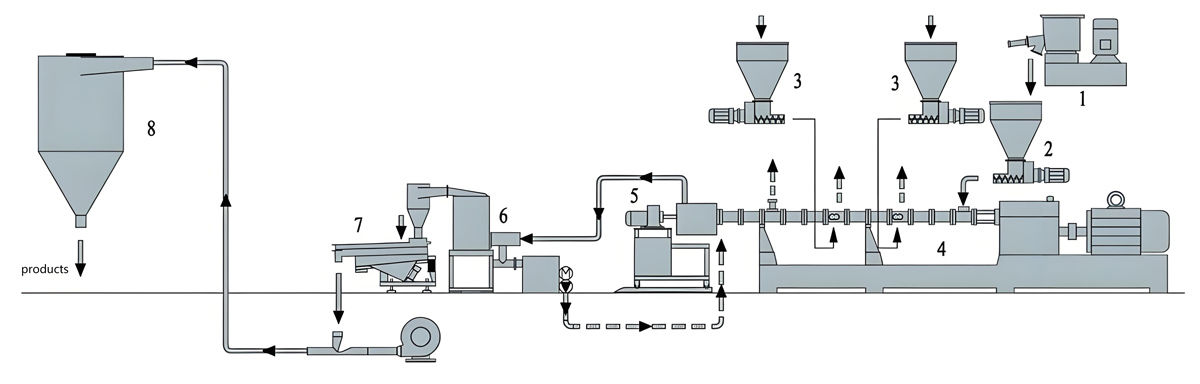
LDPE masterbatch extruder
Kerke’s masterbatch extruder can be used to produce LDPE masterbatch. Our LDPE masterbatch extruder has multiple models to choose from, which can meet different production requirements.
-

Laboratory Twin Screw Extruder
When will you need a lab twin screw extruder? If you want to make trials and tests of…
-
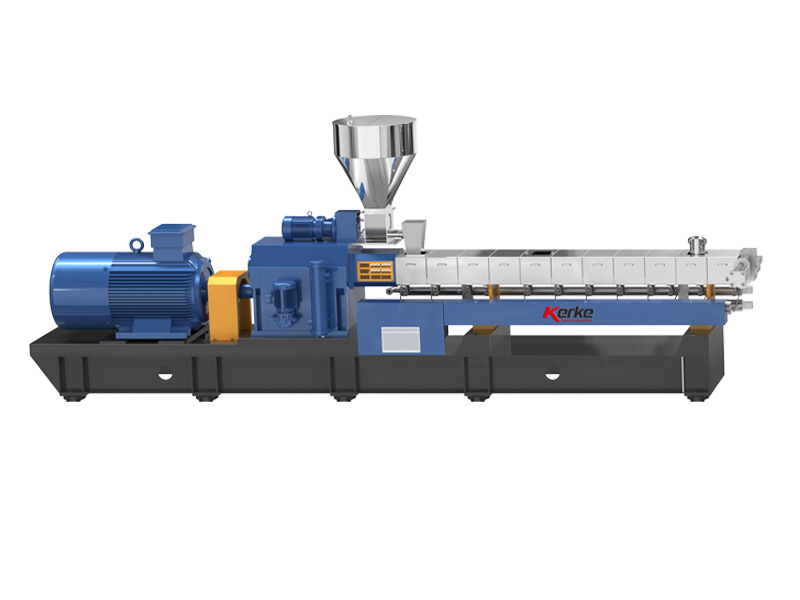
Parallel Twin Screw Extruder
Our Parallel Co-rotating twin screw extruder is designed for compounding and masterbatch making with an output capacity from…
-
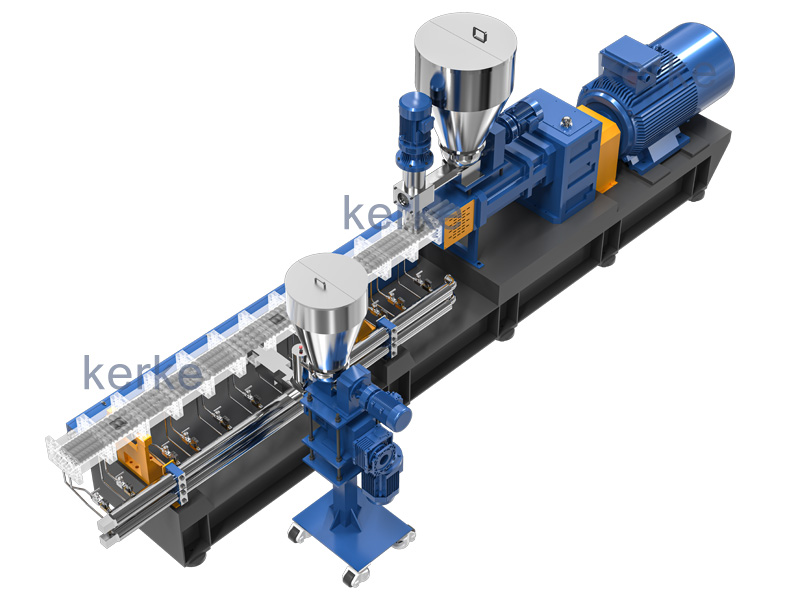
Triple (3 screws) Extruder
3 Screws extruder is a new technology that has many advantages. The triple screw extruder is mainly used…
-
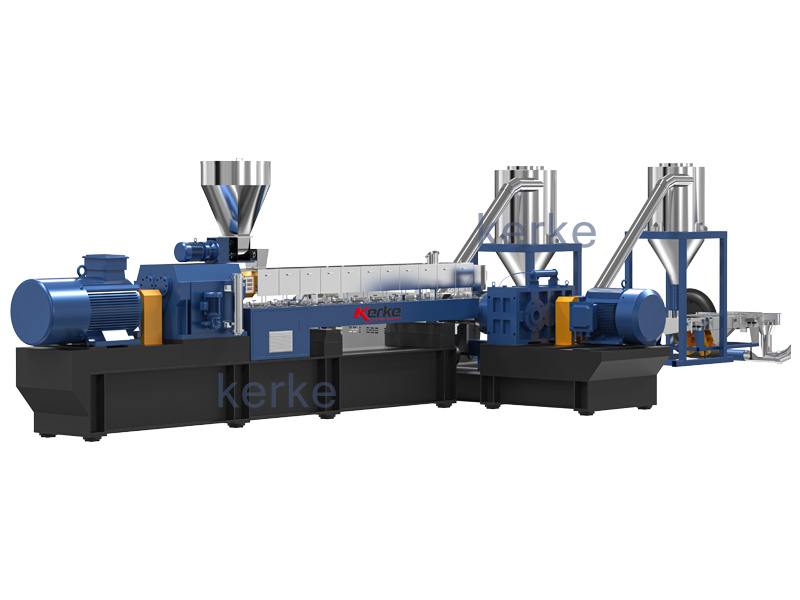

Double-Stage Extrusion System
Mother-baby extrusion system is designed for special materials which can not process on one stage extruder, the first…
-
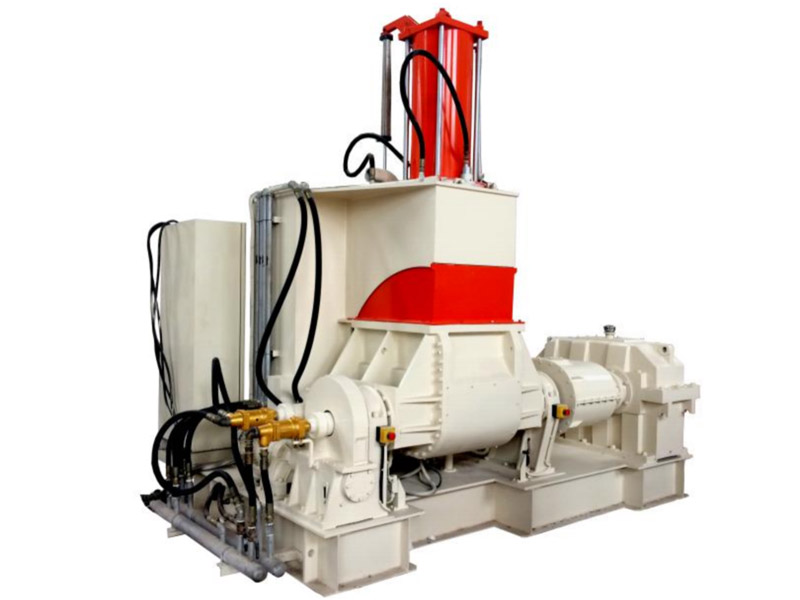

Banbury Kneader Compounding Line
Our kneader + extruder is designed for making special applications with an output capacity from 30kg/h to 1000kg/h.…
-
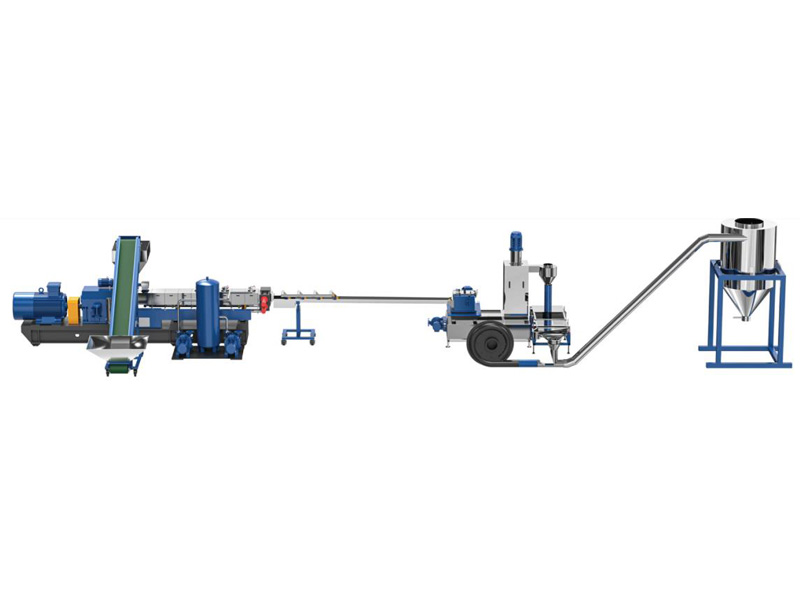
Cutting System / Pelletizing System
Different material needs different cutting system, Kerke provides all kinds of cutting system, here is the explanation of…
Application
LDPE masterbatch has good flexibility, transparency, and low temperature resistance, and is widely used in various fields. The following are its main application areas:
Packaging field
Film packaging: In terms of food packaging, such as packaging films for bread, candy, vegetables, etc., films made of LDPE masterbatch have good flexibility and transparency, which can protect food from external pollution and display the appearance of food. LDPE masterbatch is often used as the outer packaging film for daily necessities such as shampoo and shower gel. Its puncture resistance and chemical resistance ensure that the products are not damaged during storage and transportation.
Injection molding packaging: When producing injection molded packaging products such as plastic turnover boxes and plastic trays, adding LDPE masterbatch can improve the toughness and impact resistance of the products, making them more durable and suitable for frequent use in logistics and warehousing fields.
Agriculture
Agricultural film: LDPE masterbatch is an important raw material for producing agricultural films, such as greenhouse films, mulching films, etc. The greenhouse film needs to have good transparency, insulation, and weather resistance, and LDPE masterbatch can meet these requirements to help crops grow in a suitable environment. Plastic film requires good coverage and moisture retention properties. Plastic film made from LDPE masterbatch can effectively maintain soil moisture, increase soil temperature, and promote crop root development.
Irrigation equipment: In the production of drip irrigation pipes, sprinkler irrigation pipes and other equipment for agricultural irrigation, the use of LDPE masterbatch can make the products have good flexibility and corrosion resistance, adapt to different agricultural environments and irrigation needs, and extend the service life of irrigation equipment.
Medical field
Medical packaging: The packaging of medical products, such as syringes, infusion sets, drug packaging, etc., often uses films or containers made of LDPE masterbatch. LDPE masterbatch has good hygiene and barrier properties, ensuring that medical products are not contaminated during storage and transportation, while also facilitating product opening and use.
Medical supplies: Some medical catheters, protective gloves, and other medical supplies also use LDPE masterbatch. It can make these products have good softness and elasticity, meet ergonomic requirements, improve patient comfort, while ensuring product safety and reliability.
Other fields: In the wire and cable industry, LDPE masterbatch can be used to produce insulation layers and sheaths for wires and cables. With its good insulation performance and low temperature resistance, it protects wires and cables from external environmental influences and ensures the safety and stability of power transmission. In the toy manufacturing industry, LDPE masterbatch can be used to produce various plastic toys, such as toy balls, toy cars, etc., giving toys good flexibility and safety, suitable for children’s use.