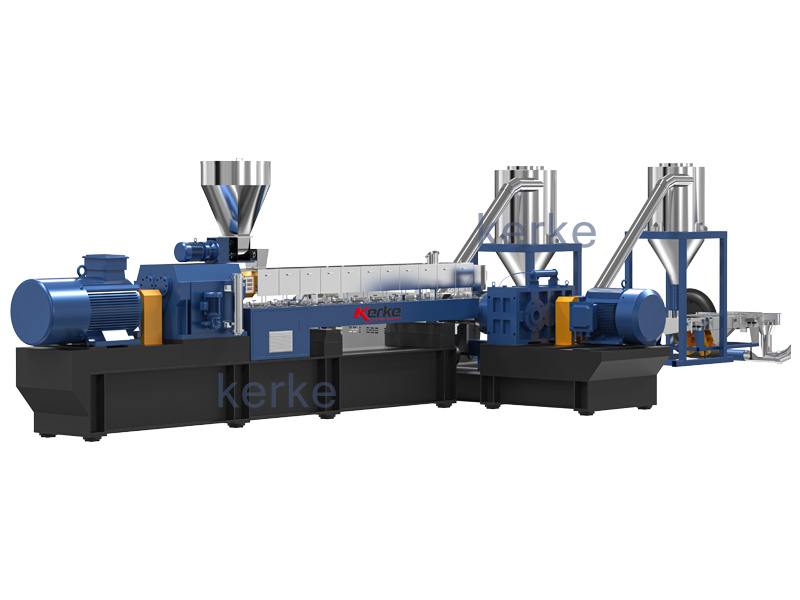
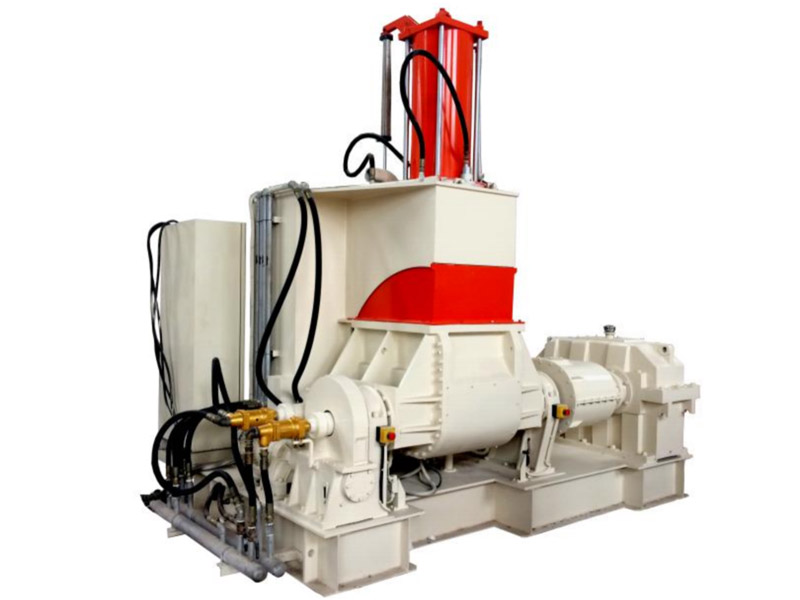
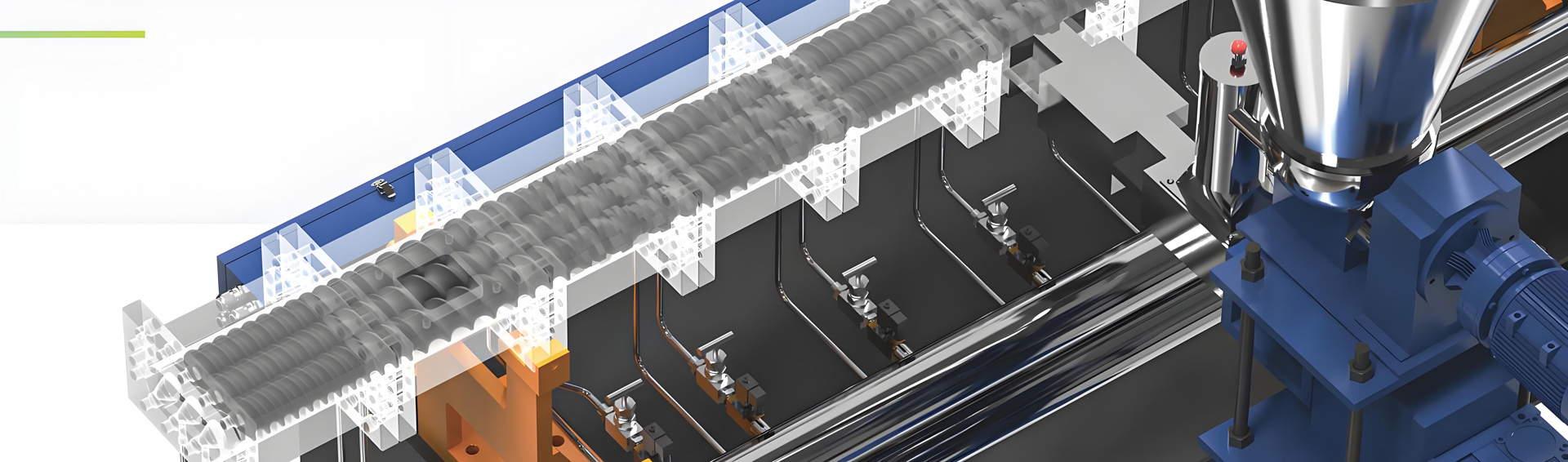
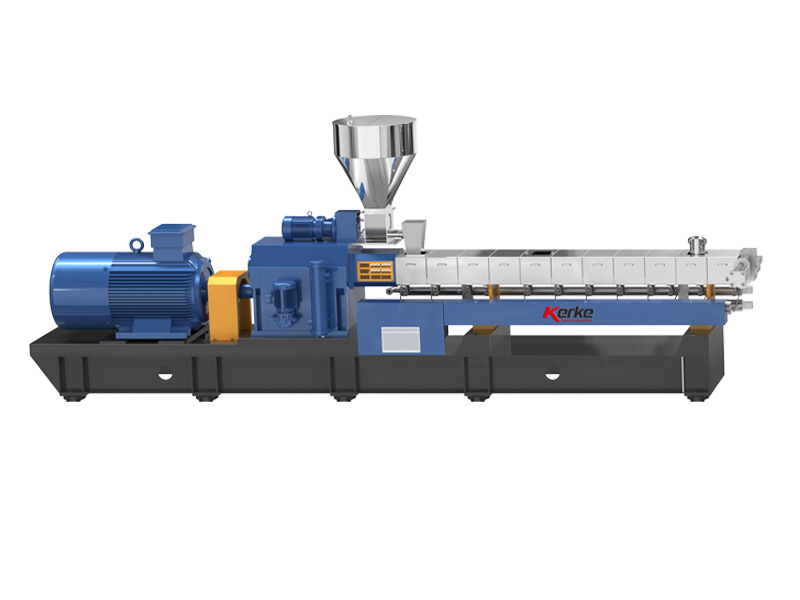
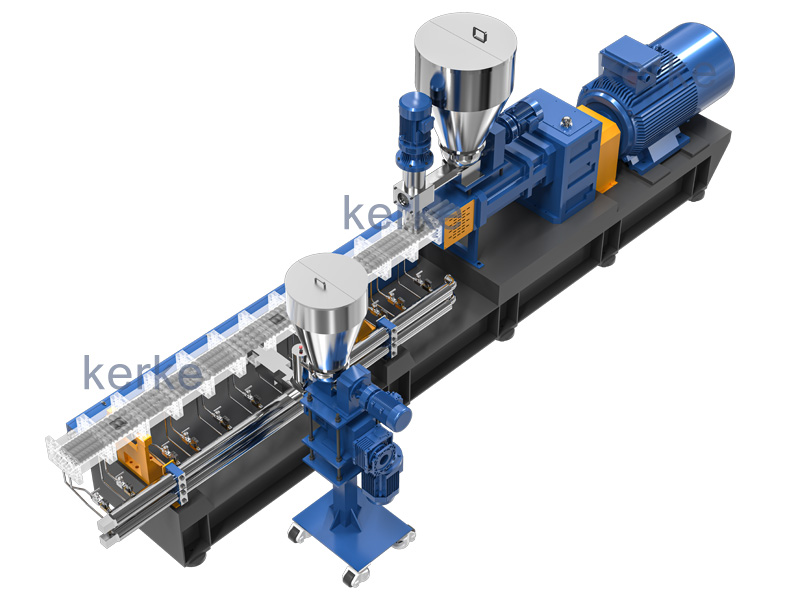
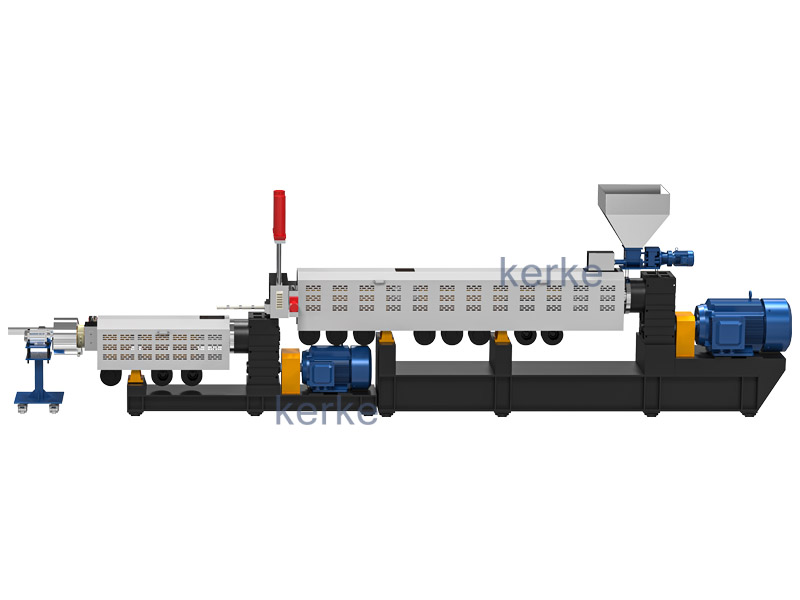
“Engineering plastic” means “engineering plastic” and is a high-performance synthetic resin with high durability and heat resistance. Among them, those with particularly high performance are called “super engineering plastics” and are used for industrial parts that require high functions.

Properties of Engineering Plastics
- Abrasion resistance.
- Chemical resistance.
- Dimensional stability.
- Electrical properties.
- Flammability.
- Food compatibility.
- Impact strength.
- Min/Max operating temperature (Thermal Resistance)
Engineering Plastics
Engineering plastics refer to industrial plastics used as industrial parts or shell materials. They are plastics with excellent strength, impact resistance, heat resistance, hardness and aging resistance. Common engineering plastics include the following:
Polyamide (PA): also known as nylon, has good wear resistance, self-lubrication and corrosion resistance, high mechanical strength and good impact toughness. It is widely used in automotive parts, machinery manufacturing, electronic appliances and other fields, such as automobile engine hoods, gears, bearings, electrical appliance housings, etc.
Polycarbonate (PC): has excellent impact resistance, transparency and heat resistance, can maintain good mechanical properties in a wide temperature range, and is often used in the manufacture of electronic appliances, optical instruments, automobile windows, protective masks and other products.
Polyoxymethylene (POM): has high hardness, high rigidity, high wear resistance and good fatigue resistance, good dimensional stability, and is widely used in machinery manufacturing, automobiles, home appliances and other industries. It can be used to manufacture precision parts such as gears, bearings, cams, valves, etc.
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO): It has outstanding insulation properties, water resistance, high temperature stability and mechanical properties, and is suitable for electronic appliances, automobiles and other fields, such as electronic equipment housings, circuit boards, automotive sensor components, etc.
Polyesters: including polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polybutylene terephthalate (PBT). PET has good mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and gas barrier properties, and is often used in fibers, beverage bottles, films, etc.; PBT has high heat resistance, high toughness, and good molding and processing properties, and is widely used in electronic appliances and automotive parts, such as sockets, switches, and car bumpers.
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA): commonly known as organic glass, it has excellent transparency, good weather resistance and mechanical properties, is easy to process and shape, and is often used in optical instruments, lighting fixtures, advertising displays, aerospace and other fields.
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS): It has excellent high temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, flame retardancy and electrical insulation, high strength and high rigidity, and is mainly used in electronic appliances, automobiles, aerospace and other fields, such as electronic component packaging, automotive engine peripheral parts, etc.
Polyimide (PI): It has outstanding high temperature resistance, radiation resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, as well as excellent mechanical properties and electrical insulation properties. It is often used in high-end fields such as aerospace, electronics, precision machinery, such as aircraft engine parts, integrated circuit substrates, high-temperature bearings, etc.