PTFE masterbatch is a granular raw material mainly composed of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which has various excellent properties and is widely used in various fields such as chemical, electronic and electrical, and medical industries. With the continuous growth of global demand for high-performance materials, the PTFE masterbatch market is also showing a good development trend. The global market size of fluoropolymer masterbatch is expected to reach 520 million US dollars in 2024, with an average annual compound growth rate of over 3.5% between 2024 and 2032.

Types
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) masterbatch is usually classified according to its application, performance characteristics, and added components, and there are mainly the following types:
Universal PTFE masterbatch
This is the most common type, possessing the basic characteristics of PTFE, such as excellent chemical corrosion resistance, low friction coefficient, good electrical insulation, and high temperature resistance.
Suitable for various fields that have basic requirements for PTFE performance, such as ordinary plastic modification, coating additives, etc., it can improve the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and self-lubricating performance of products.
Enhanced PTFE masterbatch
Glass fiber, carbon fiber, graphite and other reinforcing materials are added to PTFE resin to improve its mechanical strength, hardness, wear resistance and other properties.
Commonly used for manufacturing high-performance mechanical components such as bearings, piston rings, seals, etc., which can withstand higher pressure and friction and extend their service life.
Conductive PTFE masterbatch
By adding conductive fillers such as carbon black, metal powder, etc., PTFE masterbatch is made to have good conductivity.
Mainly used in situations that require special requirements such as electrostatic discharge and electromagnetic shielding, such as electronic device casings, packaging materials, and components in production environments that are sensitive to static electricity, it can effectively prevent the accumulation of static electricity and electromagnetic interference.
Lubricating PTFE masterbatch
This type of masterbatch usually contains an appropriate amount of lubricant, which further reduces the friction coefficient of PTFE and improves its lubrication performance.
Commonly used in manufacturing various products that require low friction performance, such as plastic guides, conveyor belts, textile machinery components, etc., it can reduce energy loss and improve equipment operating efficiency.
Radiation resistant PTFE masterbatch
After special formula design and processing, it has good radiation resistance performance.
Mainly used in nuclear energy, aerospace and other fields, materials need to withstand high-intensity radiation without performance degradation in these environments, and can meet the requirements of related equipment and components under special working conditions.
Formula ratio
The formula ratio of PTFE masterbatch may vary depending on different types and application requirements. The following are examples of approximate formula ratios for several common types of PTFE masterbatch:
Universal PTFE masterbatch
PTFE resin: 80% -95%
Dispersant: 3% -10%
Antioxidants: 0.5% -2%
Other additives: 0.5% -5% (such as anti-aging agents, lubricants, etc.)
Enhanced PTFE masterbatch
PTFE resin: 60% -80%
Reinforcement material: 15% -30% (such as glass fiber, carbon fiber, etc.)
Coupling agent: 1% -5% (used to enhance the bonding between the material and PTFE resin)
Dispersant: 3% -8%
Other additives: 1% -5% (such as antioxidants, lubricants, etc.)
Conductive PTFE masterbatch
PTFE resin: 70% -90%
Conductive filler: 5% -20% (such as carbon black, metal powder, etc.)
Dispersant: 3% -10%
Other additives: 1% -5% (such as antioxidants, antistatic agents, etc.)
Lubricating PTFE masterbatch
PTFE resin: 75% -90%
Lubricant: 5% -15% (such as silicone oil, fatty acid esters, etc.)
Dispersant: 3% -10%
Other additives: 1% -5% (such as antioxidants, etc.)
Radiation resistant PTFE masterbatch
PTFE resin: 70% -85%
Radiation resistant additives: 10% -20% (such as certain metal oxides, rare earth compounds, etc.)
Dispersant: 3% -10%
Other additives: 1% -5% (such as antioxidants, etc.)
It should be noted that the above formula ratios are for reference only. In actual production, optimization and adjustment need to be made based on specific product requirements, production processes, and the performance of raw materials. At the same time, there may be certain differences in the formulas of different manufacturers.
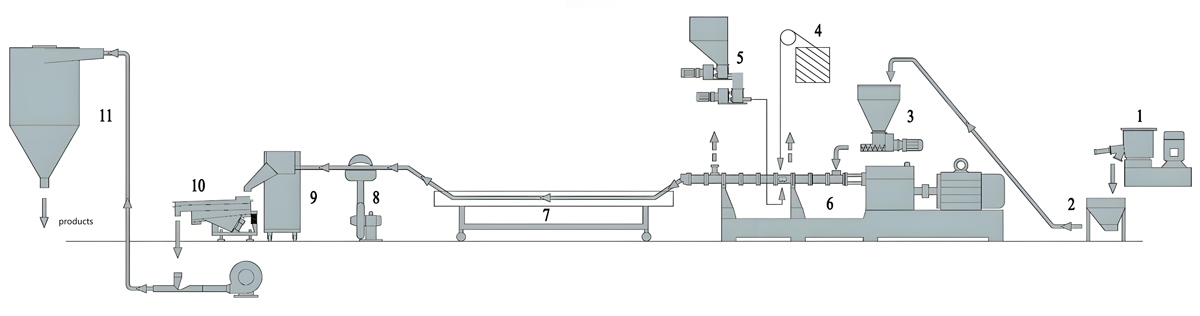
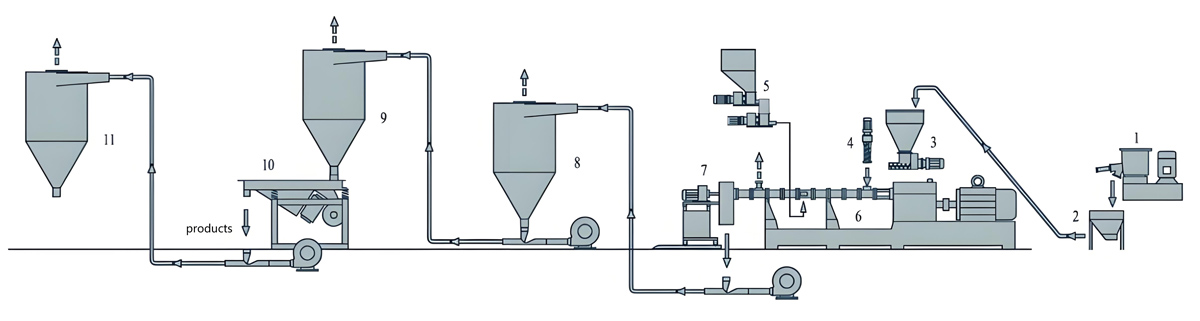
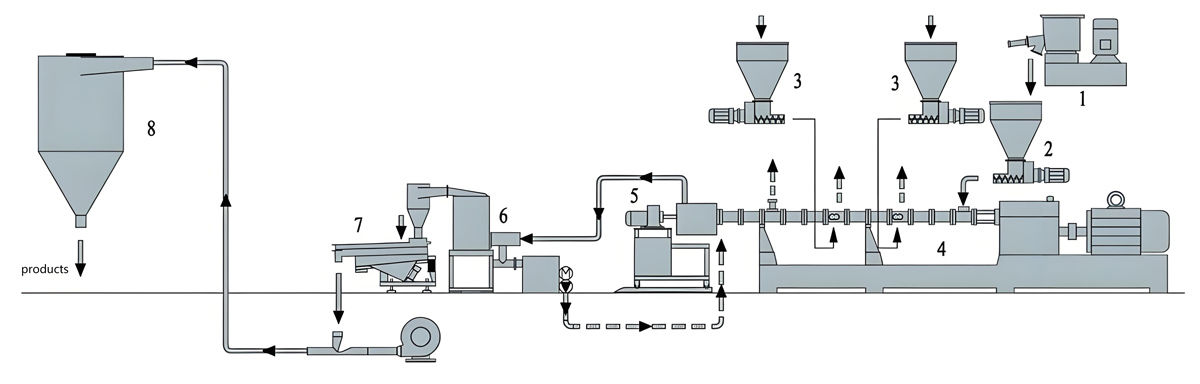
Production process
The production process of PTFE masterbatch usually includes multiple steps such as raw material preparation, mixing, extrusion, cooling, granulation, etc. The following is a specific introduction:
1. Raw material preparation
Choose the appropriate PTFE resin and prepare corresponding additives based on the type of masterbatch, such as dispersants, antioxidants, reinforcing materials, conductive fillers, lubricants, radiation resistant additives, etc. Ensure that the purity, particle size, performance, and other indicators of the raw materials meet production requirements, and perform drying treatment to remove moisture and prevent the generation of bubbles or affecting product performance during processing.
2. Mixing
Add PTFE resin and various additives to the high-speed mixer according to the set formula ratio for thorough mixing. By stirring, the additive is evenly dispersed in the PTFE resin to ensure consistency in the properties of the masterbatch. For some difficult to disperse additives, pre dispersion or special mixing processes may be required, such as adding co dispersants or extending mixing time.
3. Extrusion
Add the mixed materials into the extruder. The extruder gradually melts and plasticizes the material inside the barrel through heating and the rotation of the screw. PTFE has a high melting point and usually needs to be processed at temperatures above 300 ℃. Therefore, the heating system and screw design of the extruder need to meet the processing requirements of PTFE. During the extrusion process, it is necessary to control parameters such as temperature, screw speed, and pressure to ensure that the material can be evenly extruded and achieve good plasticizing effect.
4. Cooling
The material extruded from the extruder is in a molten state and requires rapid cooling and shaping through a cooling device. There are two common cooling methods: air cooling and water cooling. Air cooling is the use of air convection to remove heat, gradually cooling and hardening materials; Water cooling is the process of cooling the extruded material through a water tank or spray device, with a fast cooling rate. However, attention should be paid to controlling the cooling water temperature to avoid internal stress or surface defects in the product caused by rapid cooling.
5. Granulation
The cooled material is granulated as needed. There are various granulation methods, commonly including hot cutting granulation and cold cutting granulation. Hot cutting granulation is the process of cutting materials into granules using a rotating tool while they are in a hot and soft state; Cold cutting granulation is the process of cooling the material to room temperature before cutting and granulation. During the granulation process, it is necessary to control the size, shape, and uniformity of the particles to meet the needs of different users.
6. Screening and packaging
Screen the PTFE masterbatch after granulation to remove particles that are too large or too small, as well as potential impurities. Then, the mother granules that meet the requirements are packaged, usually in sealed packaging, to prevent them from absorbing moisture or being contaminated by other factors, which may affect their performance and effectiveness.
Throughout the entire production process, it is necessary to strictly control the process parameters of each link and conduct quality testing to ensure that the PTFE masterbatch produced has stable performance and good quality. At the same time, due to the difficulty of PTFE processing, the production process also needs to be optimized and adjusted according to the actual situation to adapt to different product requirements and production conditions.
Production equipment
The PTFE masterbatch production equipment mainly includes mixing equipment, extrusion equipment, cooling equipment, granulation equipment, screening equipment, etc. The following is a specific introduction:
1. Hybrid equipment
High speed mixer: used to thoroughly mix PTFE resin with various additives. It has high-speed rotating stirring blades that can achieve uniform mixing of materials in a short period of time. The mixing degree can be controlled by adjusting the stirring speed and time.
Dual planetary mixer: For some formulas that require high mixing uniformity, dual planetary mixer is a commonly used equipment. Its unique planetary stirring structure can generate complex motion trajectories of materials during the mixing process, achieving more thorough and uniform mixing, especially suitable for additives with less addition but strict dispersion requirements.
2. Extrusion equipment
Single screw extruder: suitable for producing ordinary universal PTFE masterbatch. Its structure is simple and easy to operate. The material is pushed forward by the rotation of the screw and melted and plasticized under the action of heating and shearing. But for high viscosity materials such as PTFE, the length to diameter ratio and compression ratio of the screw need to be specially designed to ensure that the material can be fully plasticized and extruded.
Twin screw extruder: commonly used for producing high-performance or specially formulated PTFE masterbatch. The twin-screw extruder has good material conveying capacity and mixing effect, which can more effectively disperse additives and enhance materials, and improve the uniformity of masterbatch performance. Moreover, it can adapt to different production needs, such as higher output and more complex formulas, by adjusting the combination of screws and process parameters.
3. Cooling equipment
Air cooling system: composed of fans, air ducts, etc., it cools the extruded material through forced air convection. The air-cooled system has a simple structure, low cost, and is suitable for situations where cooling speed is not required. It can avoid the problem of residual moisture caused by water cooling and is beneficial for maintaining the stability of PTFE masterbatch performance.
Water cooling system: usually includes a water tank, sprinkler system, circulating water pump, etc. The water cooling method has a fast cooling speed and can effectively improve production efficiency, but it requires a complete water circulation and water quality treatment system to prevent impurities in the water from contaminating the product. At the same time, attention should be paid to controlling the cooling water temperature to prevent quality problems with the product.
4. Granulation equipment
Hot cutting granulator: composed of cutting tools, transmission devices, heating devices, etc. When the material is in a hot and soft state, the extruded material is cut into granules by a rotating tool. Hot cutting granulation has the advantages of high production efficiency and regular particle shape, but it causes significant wear on cutting tools, requiring regular tool replacement and precise control of cutting temperature and speed to ensure particle quality.
Cold cutting granulator: generally composed of cutting tools, feeding devices, cooling devices, and other parts. First, transport the cooled material to the cutting position, and then cut it into particles using a cutting tool. Cold cut granulation has high particle size accuracy and good surface quality, but relatively low production efficiency, making it suitable for occasions with high requirements for particle quality and low output requirements.
5. Screening equipment
Vibration screen: Using the vibration generated by a vibration motor to screen particles on the screen. By adjusting the vibration frequency, amplitude, and mesh size, PTFE masterbatch with different particle size ranges can be screened to remove oversized or undersized particles and impurities, ensuring the uniformity of product particle size.
Airflow sieve: Using airflow as the driving force, particles are screened through the sieve under the action of airflow. Airflow screening has the advantages of high screening accuracy and low clogging of the screen mesh, especially suitable for screening fine PTFE masterbatch. However, the equipment structure is relatively complex and the operating cost is high.
6. Packaging equipment
Automatic packaging machine: capable of automatically completing packaging processes such as measurement, filling, and sealing. According to different packaging specifications and requirements, different types of automatic packaging machines can be selected, such as powder packaging machines, granule packaging machines, etc. Automatic packaging machines can improve packaging efficiency, ensure consistency in packaging quality, and reduce pollution and errors caused by manual operations.
In addition to the main equipment mentioned above, auxiliary equipment such as raw material drying equipment, measuring equipment, and conveying equipment may also be required during the production process of PTFE masterbatch to ensure the smooth progress of the entire production process.
PTFE masterbatch extruder
Kerke’s masterbatch extruder can be used to produce PTFE masterbatch. Our PTFE masterbatch extruder has multiple models to choose from, which can meet different production requirements.
-

Laboratory Twin Screw Extruder
When will you need a lab twin screw extruder? If you want to make trials and tests of…
-
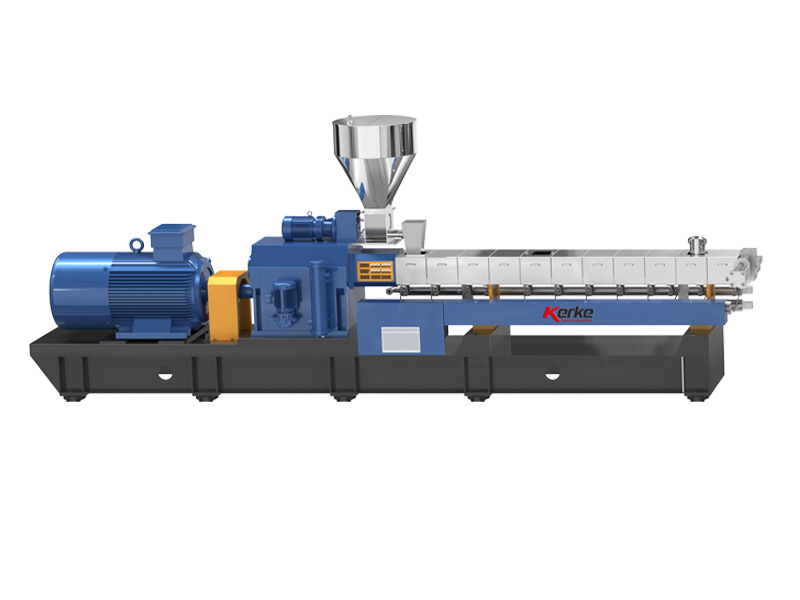
Parallel Twin Screw Extruder
Our Parallel Co-rotating twin screw extruder is designed for compounding and masterbatch making with an output capacity from…
-
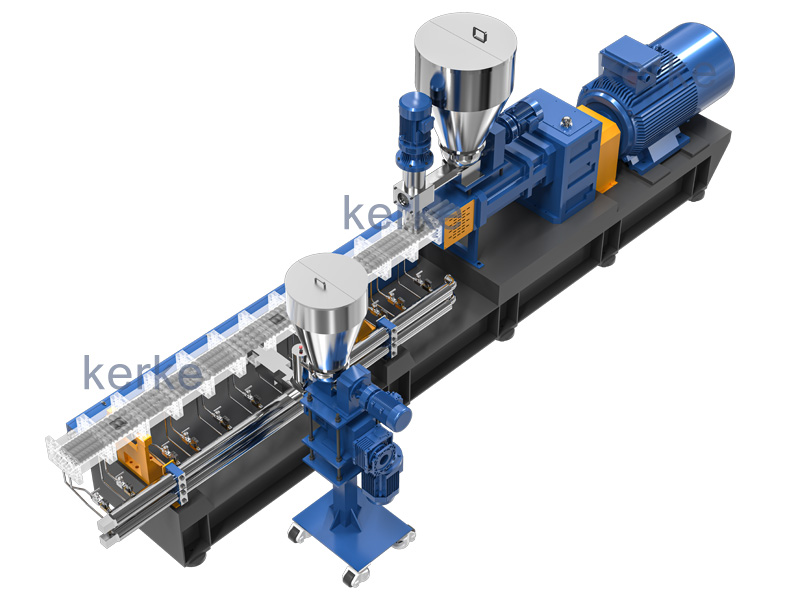
Triple (3 screws) Extruder
3 Screws extruder is a new technology that has many advantages. The triple screw extruder is mainly used…
-
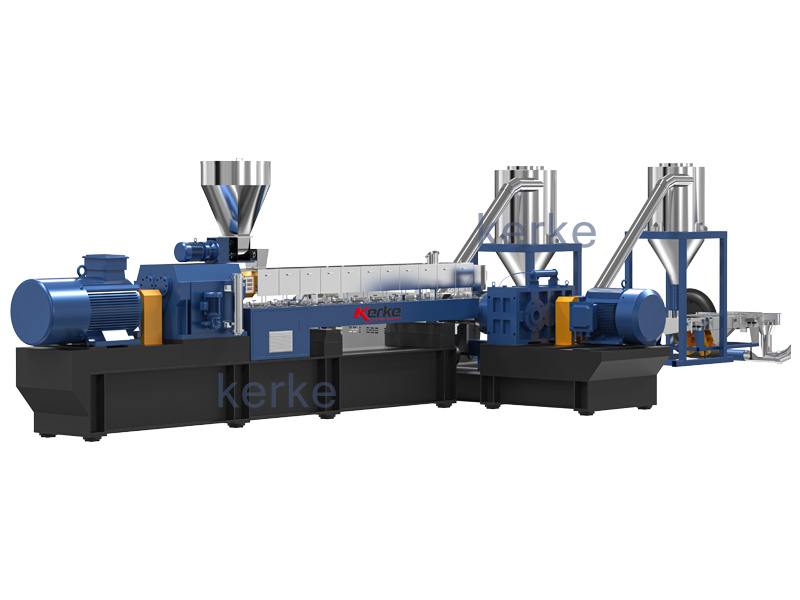

Double-Stage Extrusion System
Mother-baby extrusion system is designed for special materials which can not process on one stage extruder, the first…
-
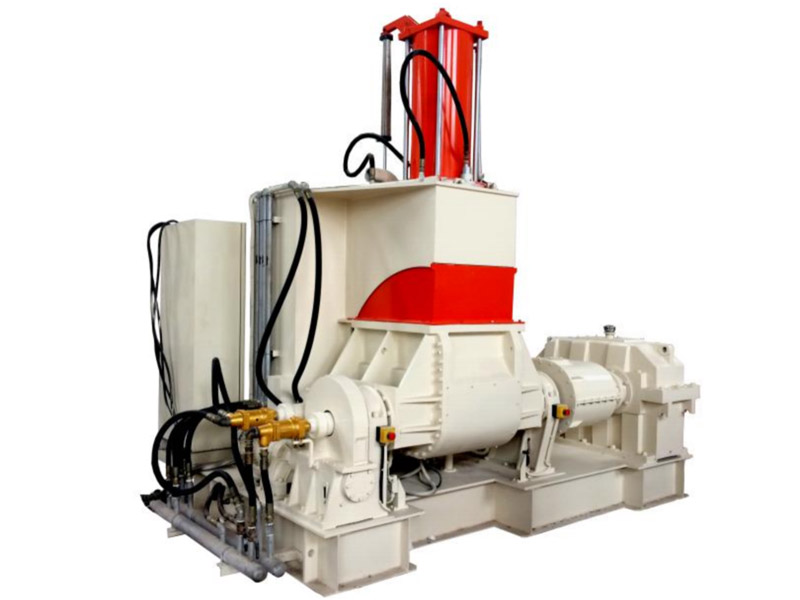

Banbury Kneader Compounding Line
Our kneader + extruder is designed for making special applications with an output capacity from 30kg/h to 1000kg/h.…
-
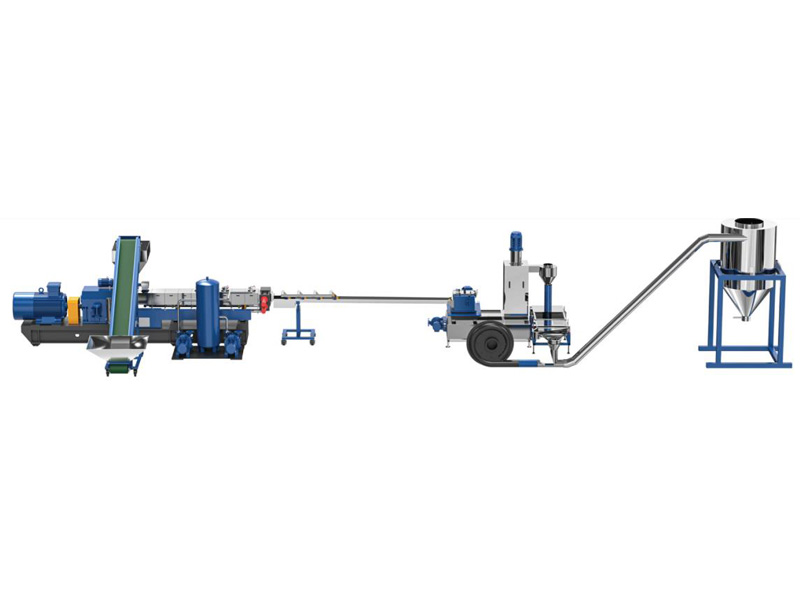
Cutting System / Pelletizing System
Different material needs different cutting system, Kerke provides all kinds of cutting system, here is the explanation of…
Related requirements
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) has characteristics such as high melting point, high viscosity, and low friction coefficient. Therefore, when producing PTFE masterbatch, the extruder has the following special requirements:
Screw design
Length to diameter ratio: The plasticization of PTFE requires a longer time and greater shear force, so it is usually necessary to use screws with a larger length to diameter ratio, usually between 25-32. This can increase the residence time of the material in the screw, allowing it to fully melt and plasticize.
Compression ratio: Due to the significant volume change of PTFE before and after melting, an appropriate compression ratio is required to achieve material compaction and plasticization. The compression ratio is generally between 3-5, and the specific value needs to be adjusted according to the type and formula of PTFE.
Thread shape: In order to effectively transport and shear PTFE materials, the thread shape of the screw is usually designed with a mutation or gradual change. Mutant threads can generate significant shear forces in a short distance, which is beneficial for the plasticization of PTFE, but can cause significant damage to the material; Gradient threads are relatively gentle and suitable for PTFE formulations that are sensitive to shear.
Heating and cooling system
Heating method: The processing temperature of PTFE is relatively high, generally between 300 ℃ and 400 ℃, so the extruder needs to be equipped with an efficient heating system. The commonly used heating methods include electric heating and thermal oil heating. The electric heating method has the advantages of fast heating speed and precise temperature control; Thermal oil heating has the characteristics of uniform temperature and good stability, and is suitable for large extruders.
Cooling system: In the extrusion process, a good cooling system is required to prevent material overheating. The cooling system usually adopts water cooling or air cooling, which is achieved by setting cooling jackets or cooling fans on the barrel. The design of the cooling system should ensure uniform cooling and avoid local overheating or overcooling, which may affect product quality.
Material selection
Barrel and screw material: Due to PTFE’s strong chemical corrosiveness, the barrel and screw of the extruder need to be made of corrosion-resistant materials such as nickel based alloys, stainless steel, etc. These materials not only have good corrosion resistance, but also can withstand high temperature and high pressure, ensuring the normal operation of the extruder.
Sealing material: In order to prevent PTFE material leakage, the sealing material of the extruder needs to have high temperature resistance, wear resistance, and good sealing performance. Common sealing materials include polytetrafluoroethylene, carbon fiber, etc. These materials can be used to make sealing rings, gaskets, and other components, which are installed at the connection between the barrel and screw, as well as at the feeding port.
Drive system
Power requirements: The high viscosity of PTFE requires a large amount of power for the extrusion process, so the transmission system of the extruder needs to have sufficient torque and power. Generally, high-power motors and reducers are used to drive the screw to ensure stable operation under high loads.
Transmission accuracy: In order to ensure the stability of extrusion volume and consistency of product quality, the transmission system needs to have high transmission accuracy. The use of high-precision gear transmission or synchronous belt transmission can reduce transmission errors and improve the stability of screw speed.
Control system
Temperature control: Accurate temperature control is the key to producing PTFE masterbatch. The control system of the extruder needs to be equipped with high-precision temperature sensors and temperature controllers, which can monitor and adjust the temperature of each section of the barrel in real time, ensuring that the temperature fluctuation is within ± 1 ℃.
Screw speed control: The screw speed directly affects the extrusion amount and plasticization effect of the material, so precise control of the screw speed is required. The control system usually adopts variable frequency speed regulation technology, which can flexibly adjust the screw speed according to production needs and has good speed stability.
Pressure control: During the extrusion process, changes in material pressure can affect the quality and yield of the product. The control system of the extruder needs to be able to monitor the extrusion pressure in real time and control the pressure stability by adjusting parameters such as screw speed and feeding amount to avoid product defects caused by excessive pressure fluctuations.
Application
PTFE masterbatch has excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, low friction coefficient, and good electrical insulation properties, and therefore has a wide range of applications in multiple fields. The following are some of the main application areas:
Plastic Modification
Improving corrosion resistance: In some plastic products that require contact with corrosive media, adding PTFE masterbatch can significantly enhance the corrosion resistance of the plastic. For example, adding PTFE masterbatch to plastic products such as chemical pipelines and storage tanks can maintain good performance and extend the service life of plastics when exposed to corrosive substances such as acids, alkalis, and salts for a long time.
Reduce friction coefficient: PTFE masterbatch can lower the friction coefficient of plastics, making them have good self-lubricating properties. This characteristic has been widely used in plastic products such as mechanical parts, bearings, and gears, which can reduce friction and wear between parts, improve mechanical efficiency, and reduce energy consumption.
Improving heat resistance: PTFE has high heat resistance, and adding PTFE masterbatch can increase the plastic’s thermal deformation temperature and long-term use temperature. For example, adding PTFE masterbatch to plastic components around car engines can maintain good dimensional stability and mechanical properties in high-temperature environments.
Wire and cable
Insulation protection: PTFE masterbatch has excellent electrical insulation performance and high and low temperature resistance, and can be used to produce insulation layers for wires and cables. In some applications that require high electrical performance, such as aerospace, military, high-end electronic equipment, etc., the insulation layer made of PTFE masterbatch can ensure the safe and reliable transmission of current in wires and cables under complex environmental conditions.
Chemical corrosion resistance: In some harsh chemical environments, such as petrochemicals, electroplating and other industries, wires and cables are easily corroded by chemical substances. The insulation layer made of PTFE masterbatch has good chemical corrosion resistance, which can protect wires and cables from corrosion and extend their service life.
Paint
Non stick coating: PTFE masterbatch is one of the key raw materials for preparing non stick coatings. In the fields of kitchenware, food processing equipment, etc., the use of non stick coatings containing PTFE masterbatch can make the surface of objects have good non stick properties, facilitate cleaning, prevent food or other substances from adhering to the surface, improve work efficiency, and also comply with food safety standards.
Anti corrosion coating: PTFE masterbatch can be used to prepare anti-corrosion coatings, which are applied to the surfaces of metals, concrete and other materials. It can effectively prevent corrosive substances such as acid, alkali and salt from corroding the substrate, protect the substrate material, and extend its service life. For example, PTFE anti-corrosion coatings have a wide range of applications in fields such as ships, bridges, and construction.
Fibre
High temperature resistant fibers: By adding PTFE masterbatch to fiber production, high-temperature resistant fiber materials can be prepared. This fiber has good heat resistance and stability, and can be used in high-temperature environments, such as in the production of high-temperature protective clothing and filter materials for aerospace, firefighting, metallurgy, and other fields.
Corrosion resistant fiber: PTFE fiber has excellent corrosion resistance and can be used to make filter cloth, separation membrane, etc. in the fields of chemical engineering, environmental protection, etc. These fiber products can work stably in corrosive media such as strong acids and alkalis, effectively filter and separate various substances, and improve production efficiency and product quality.